The 2025 Working Relations Index® (WRI®) Study results are in, and the findings are telling. The WRI Study measures the strength of the commercial relationships between Ford, General Motors, Honda, Nissan, Stellantis, and Toyota and their direct suppliers. It reflects supplier sentiment about the capability and propensity of these vehicle manufacturers to deal with macroeconomic and industry-specific issues, including tariff and trade restrictions, production and sales volatility, and product plan stability equitably with strategic partners.
The survey drew 665 responses from executives at 398 discrete companies, 68 of which were from the 100 largest North American suppliers. The anonymous online supplier survey included 16 quantitative questions measuring the characteristics of the buyers, 18 questions related to business practices, and 22 questions specific to trust, communication, mutual profitability, assistance, and hindrance or friction at the interface between the vehicle manufacturers and suppliers. In addition, it includes seven open-ended questions to capture the thoughts and the reasoning behind the respondents’ quantitative answers.
Why do customer-supplier relationships matter?
Customer-supplier relationships enable commercial partnerships to create and deliver market-leading innovation and timely, effective responses to volatile supply chain dynamics. Strong relationships promote ongoing transactional efficiency, the ability of the customer and the supplier to achieve performance goals within financial expectations and operational stability. The WRI is a tool both parties can use to identify how to improve their commercial relations, lowering the cost and risk of doing business together.
2025 results
Three of the six OEMs improved overall relationships while managing unprecedented market volatility due to changing government policies, EV program cancellations, new low-cost Chinese entry threats, uncertain sales volumes, and continued tensions over cost-recovery issues related to materials and tooling.
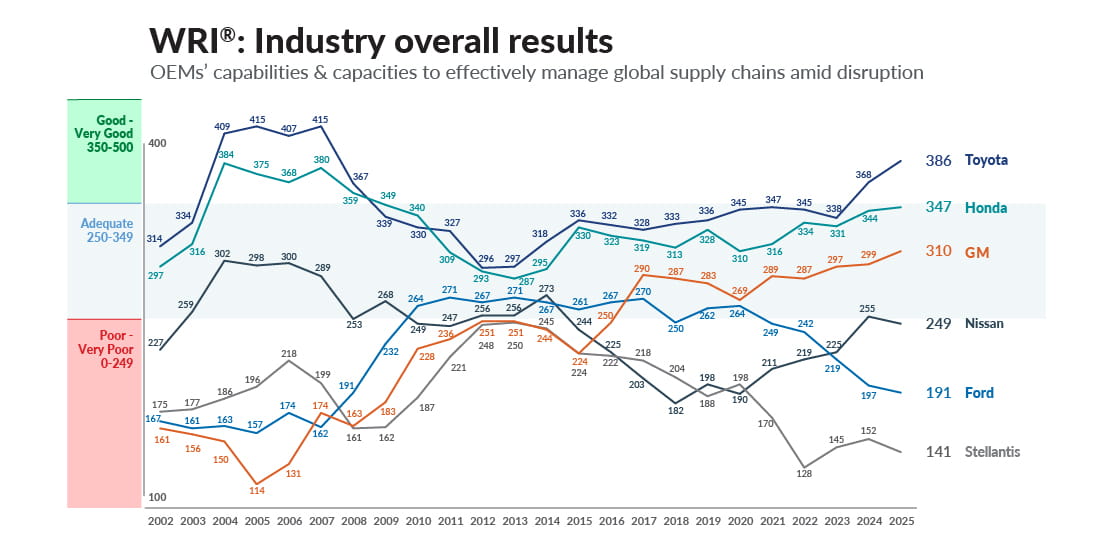
Toyota jumped 18 points to 386, which puts the automaker alone in the upper good-very good category — Toyota’s highest score in the WRI since 2007 when they topped out at 415. Honda gained 3 points and scored 347. GM gained 11 points to 310, rising above 300 for the first time. The result is especially noteworthy, given that 20 years ago, the company placed last with a WRI score of only 114, the lowest score ever recorded in the study. GM maintains third in rank behind Honda and Toyota (see full WRI graph below).
While the top performers improved, the bottom three declined. Nissan fell 6 points to 249. Ford also fell 6 points year over year, keeping the company in fifth place. Stellantis dropped 11 points and remains in last place at 141. There is a gap of 245 points between Toyota and Stellantis, the largest gap since 2008.
Top takeaways from the 2025 WRI Study
The Plante Moran team identified several prominent themes derived from the survey results. Among them:
Established relationships propelled the top three OEMs’ gains
Suppliers reported feeling like a true partner 12 times more for the top three OEMs versus the bottom three OEMs. The top three OEMs were able to lean into established relationships to jointly address with suppliers economic and industry chaos, creating more win-win outcomes.
Fundamentals come first. Trust is an outcome
Relationships improve when it’s easier to work together, and the top performers improved fundamental behaviors and processes by having:
- Purchasing VPs present and engaged.
- Buyers that are accessible, knowledgeable, and responsive.
- Payments that are made in a timely manner.
- Regular, open discussions for supplier strategic planning.
Company implications
Consistency, predictability, and alignment of strategic goals lower the perceived risk and cost to serve and drive the suppliers’ perception of customer of choice. Toyota, Honda, and General Motors remain respectively in first, second, and third in Customer of Choice, tracking their WRI score. Toyota and Honda have these attributes entrenched in their cultures, and GM is making gains in its culture as it continues to push back on lingering “old school” behaviors. However, Toyota and Honda face the challenge of maintaining those values as North American operations become more westernized. Toyota will be further tested this year with its first North American purchasing leadership change in 14 years.
Customers of choice must embody enabling behaviors that help suppliers manage the bottom-line impacts of OEM decisions and navigate the uncertainty of their “fit” in future OEM strategies. OEMs that improved ease of payments, timely and fair commercial issue resolution — particularly related to volume and program changes — and transparent, open communication for strategic long-term alignment had their Customer of Choice scores improve.
How to use the study
Customers use this study to measure the effectiveness of supplier governance strategies, cost-reduction programs, and the subsequent financial sharing of those cost savings with suppliers. This anonymous, honest data shapes purchasing, personnel onboarding, and culture training. The study’s findings help better align OEM internal functions, such as engineering, with purchasing to reduce unintended supplier costs.
Suppliers use the study to adjust their commercial strategies to preferred customers. Every OEM has good, adequate, and poor relationships. Suppliers match the level of investment, such as research and development, product engineering, or overall human resources, to the strategic value of each account. Suppliers also use results to assess their experiences with a given customer to overall supplier sentiment.





